Query
1. Query
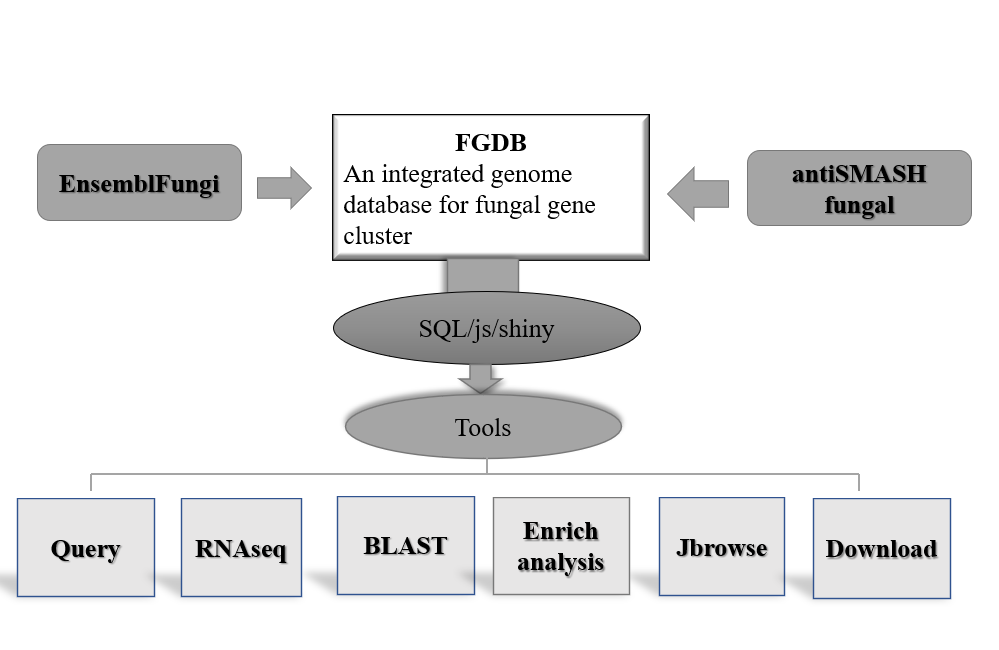
In the query module of the database, users can filter and find the
required gene clusters in a variety of ways. First, users can select
specific species as search criteria. This species selection box supports
keyword search, users only need to enter the name of the species or related
keywords, and then select the type of gene cluster, the system will automatically
retrieve the gene cluster information related to the species. The system will
return a gene cluster containing all eligible genes, and will display its complete
structural information, including the length of the gene cluster, starting position,
ending position, etc. At the same time, the system will also display the sequence
information of each gene cluster, and users can view the specific sequence content
of the gene cluster for further analysis.(Figure 1)
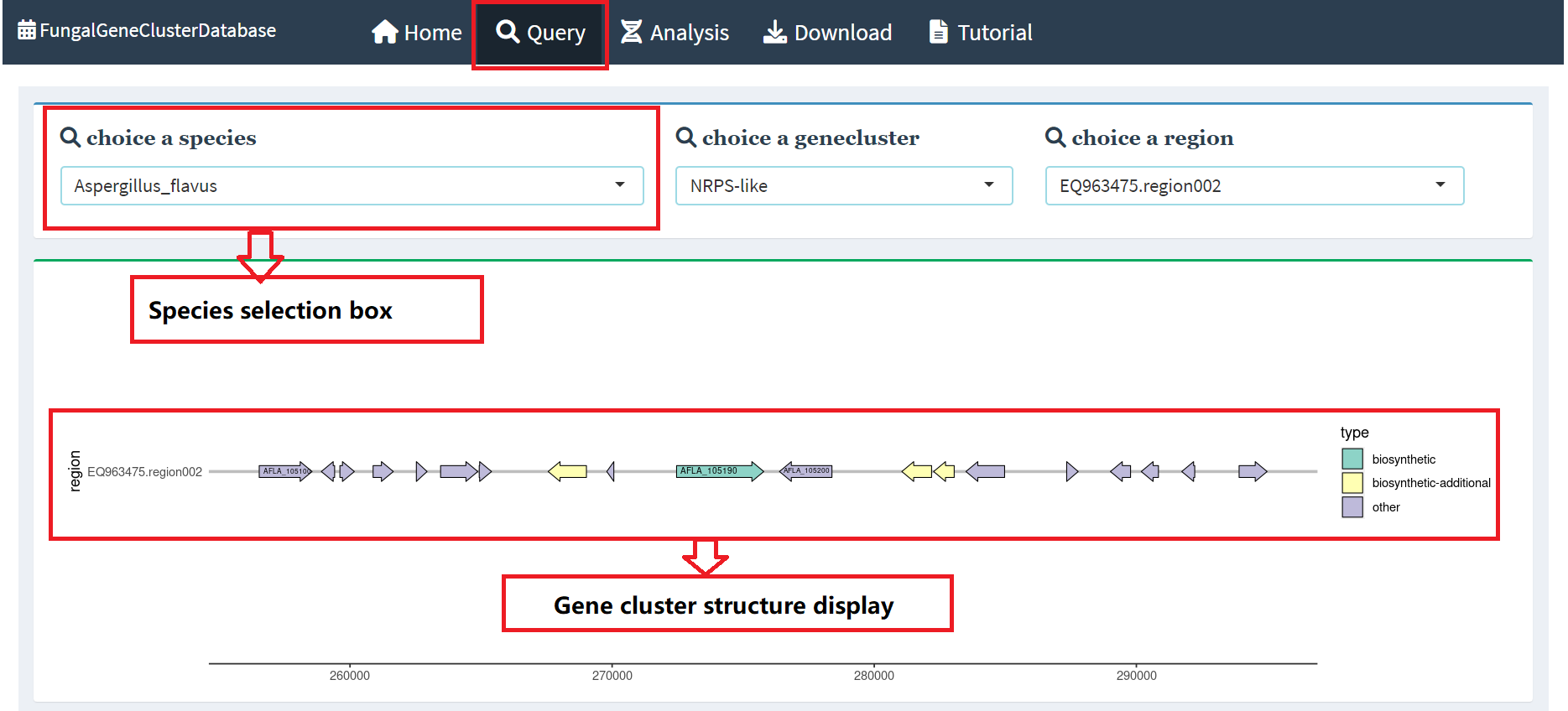
Figure 1. Query a Gene cluster
2. Gene browser
Under the gene structure display in the query interface, we present the name of
the gene, location information, and the type and region of the gene cluster in the
form of a table. Users simply click on the table above, and the Genome browser below
will display more detailed genetic information. In order to provide a more intuitive
presentation effect, we placed the resulting transcriptome data in different browser
tracks for display. This design not only beautifies the interface, but also makes it
easier for users to browse and analyze genetic information(Figure 2).
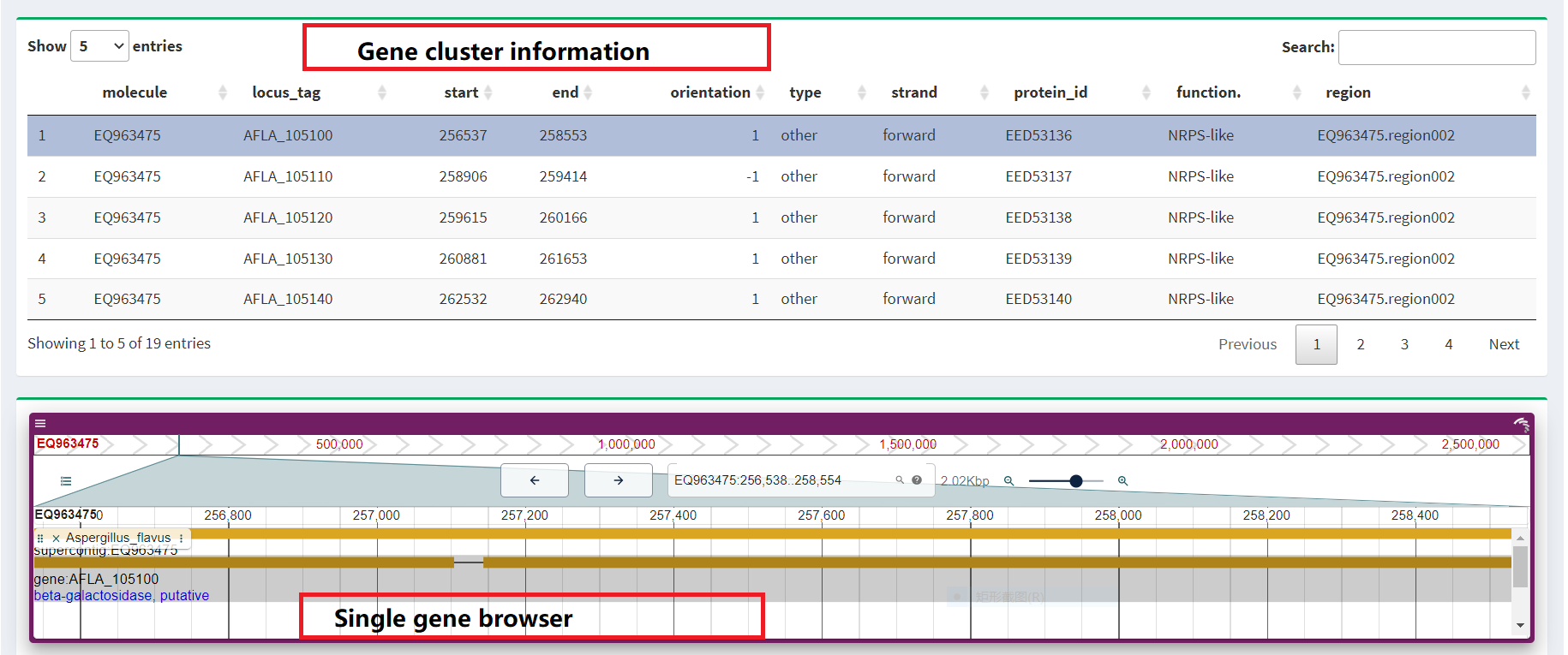
Figure 2. Gene browser
3. RNAseq data
We also provide transcriptome data collected from related species that are analyzed,
collated, and screened to eventually form gene clusters that are displayed on the interface.
At the same time, we also show the expression levels of these gene clusters so that users
can better understand their functions and regulatory mechanisms. In order to facilitate further
research, we provide links to the original data so that users can directly access and use the data.
We promise that this section will be continuously updated to keep the information and data up to date.
You can view the expression of genes of interest by clicking on the genes
in the table above.(Figure 3).
Figure 3. Transcriptome data presentation
3. Other
At the same time, we provide the user with the sequence information of each gene in the gene cluster.
Users only need to click on the corresponding gene in the table above, and the system will display the
detailed sequence information of the gene. This design makes it easier for users to view and analyze
the sequence contents of specific genes to gain further insight into their functions and
characteristics.(Figure 3).
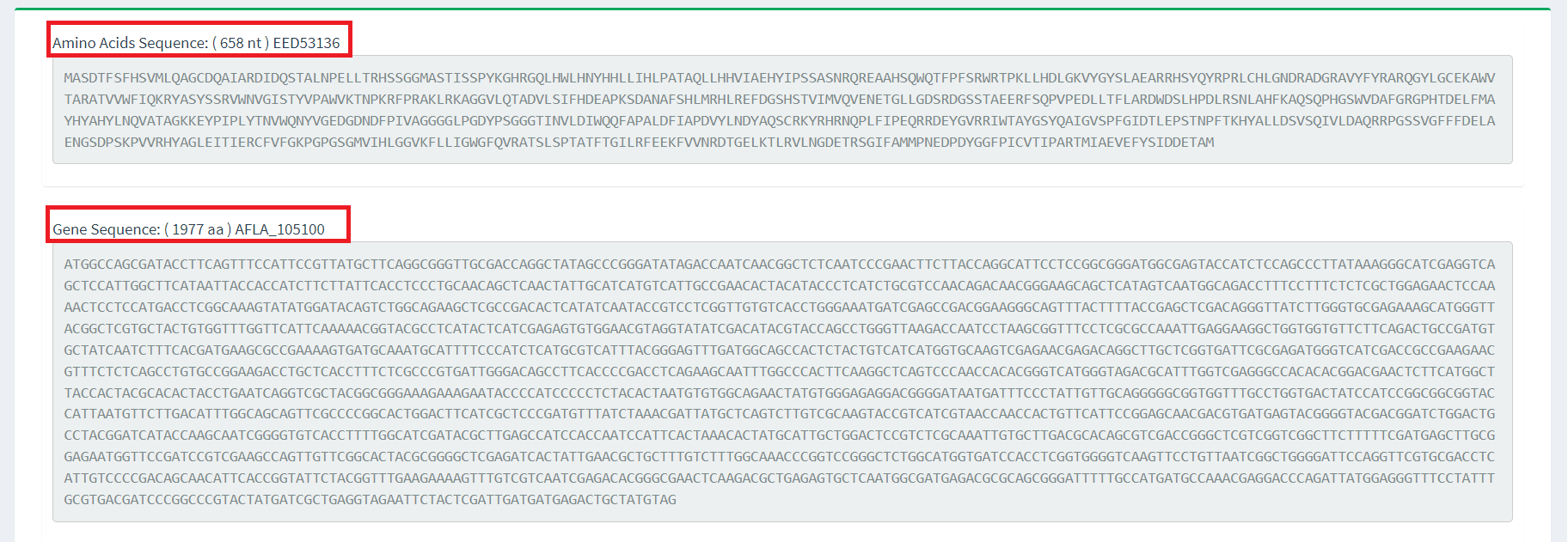
Figure 4. Gene sequence